| Japanese | English |
| vesicular sound | The sound of air inhalation can be heard. But, the sound of expiration can hardly be heard. |
| bronchial breath sound | It becomes abnormal when it is heard in the peripheral lung fields. |
| tracheal sound | Breath sound recorded on the neck. |
| coarse crackle | Crackles are caused by the passage of air through the small airways in the lung that have become sticky and adherent due to the presence of fluid, mucus, or pus. The coarser and lower-pitched the crackles sound, the higher their origin in the respiratory tree. |
| fine crackles | Crackles with a dry quality, more crisp than gurgling, are apt to occur higher in the respiratory tree. |
| wheezing | Wheezes are caused by narrowing, constriction, or spasm in the very small airways. They can occur because of asthma, congestive heart failure, fibrosis, pneumonia, and tuberculosis. |
| rhonchi | Rhonchi are low pitched, snore-like sounds. They are caused by airway secretions and airway narrowing. |
This time, lung sounds listed above will be analyzed as last time. Download the above files and try the analysis.
This is the main window of DSSF3 version 5. My PC is DELL INSPIRON 7500, and OS is Windows 2000 Professional. Sound driver is ESS Maestro, which is default of DELL PC. DSSF3 is the latest version updated on 20 March 2003.
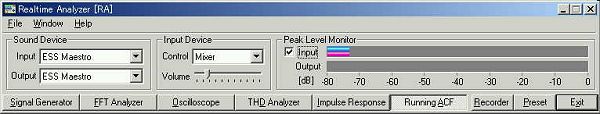
In this experiment, wave file is loaded on the Running ACF window of the Realtime Analyzer. So the input device is set to "Mixer" (or WAVE/DirectSound, the name of the device depends on the soundcard used). When the wave file is read by RA, sampling rate of the wav file is automatically detected.
Another procedure is to reproduce the sound by the Windows Media Player and to measure its output. But in this case, digital signal is converted to analog and again converted to digital inside the PC. So, the sound quality might be decreased because of the quality of the soundcard. We recommend to analyze the wav files directly.
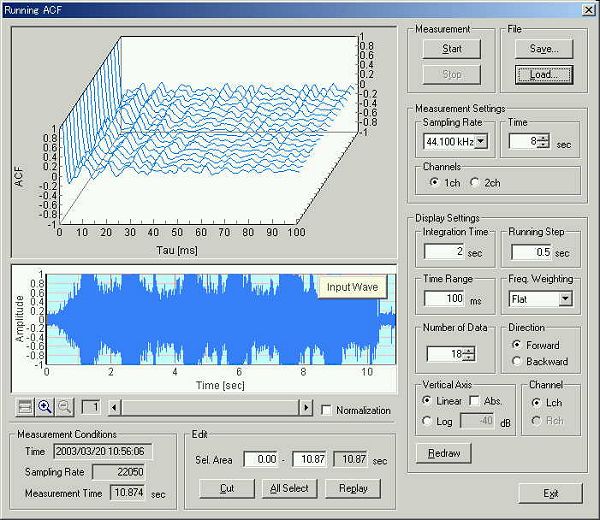
Open the running ACF window, and click the "Load" button. On the "Load Measurement Data" dialog, click the "Wave File" button.
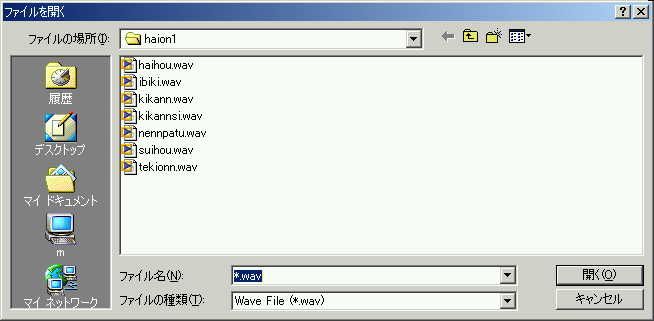
This is the wave file open dialog. Downloaded wave files are listed. First, "kikannsi.wav" (bronchial breath sound) is selected.
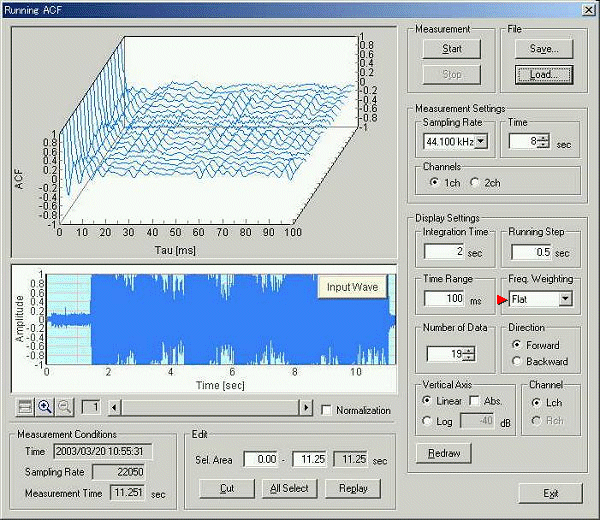
1. Normal Lung Sound (bronchial breath sound)
Data is loaded on the running ACF window. Frequency weighting is Flat in this analysis.
Note: This software is originally developed for the multi purpose acoustical measurement, for example, the room acoustics and the noise measurement. For those measurements, frequency response of the measurement system is fitted to the human ear sensitivity by A-weighting filter to analyze the sound that people actually hear. But such a filtering sometimes removes the important information for analyzing the sound itself. So, this time no frequency weighting is used.
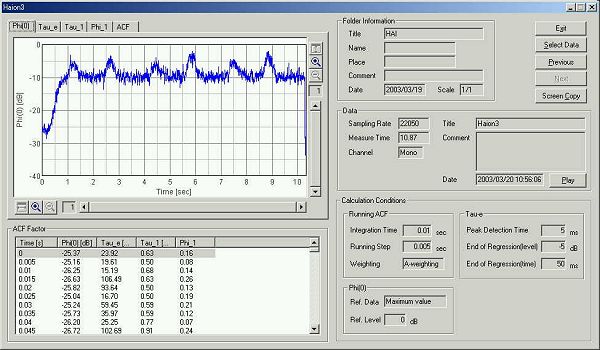
Save the loaded sound as "HAION1".
Start the Sound Analyzer (SA). Saved data will be listed in the main window of SA. Now we are ready for the analysis.
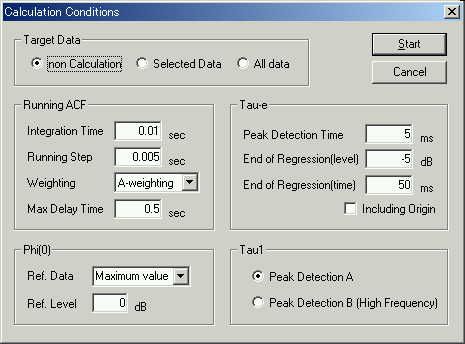
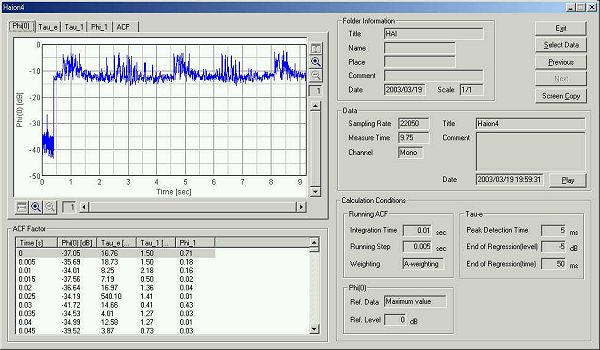
This is the calculation condition. Integration time and the running step are set to 0.01 and 0.005 s.
This is the time history of the sound level.
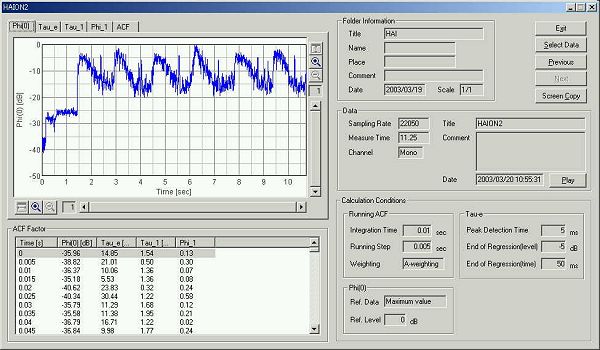
Graph images are exported by the "Screen copy" function. Attention is paid to the strange peak of the sound level.
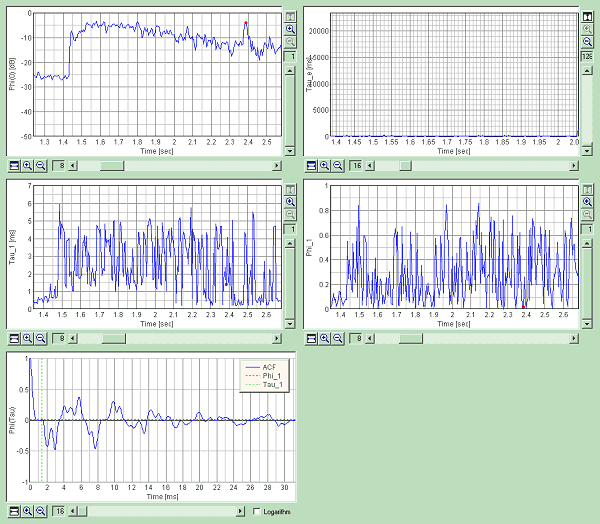
2. Normal Lung Sound (tracheal sound)
Next, tracheal sound is loaded.
This is the time course of the sound level.
Graph images are exported.
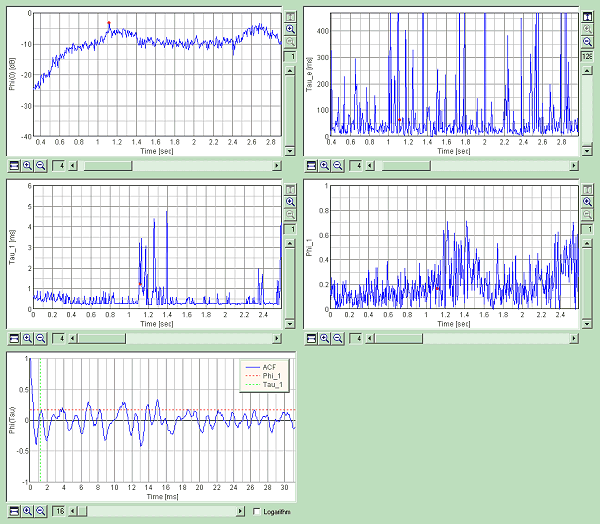
3. Abnormal Lung Sound (coarse crackle)
Next, coarse crackle is loaded. This is an abnormal sound. It expresses pneumonia and tuberculosis. More precisely, it is heard by bronchitis, pneumonia, pulmonary tuberculosis, pulmonary infarction, pulmonary suppuration, a lung congestion, the lung blister, bronchiectasis. Crackle sound is described as fine, popping, crackling, discontinuous, non-musical noises. It lasts about 10-25 ms.
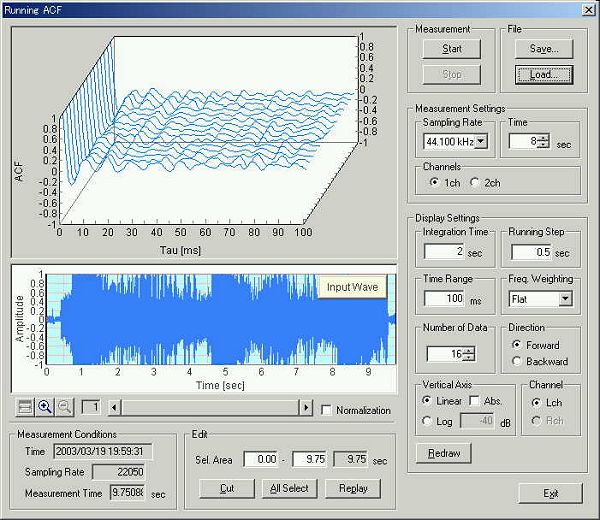
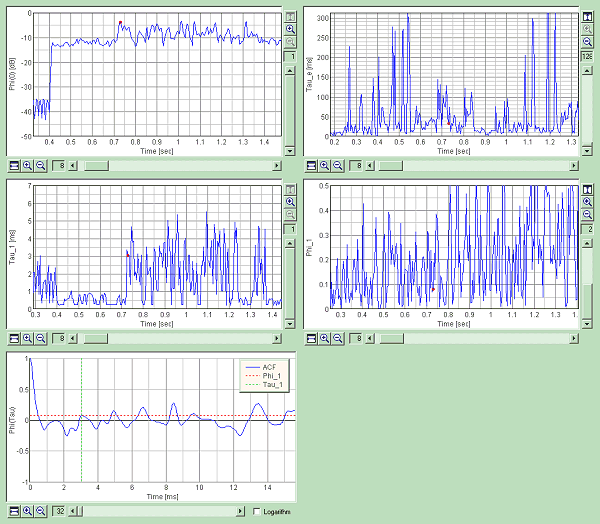
Time course of the sound level is shown below. Measurement time is 9.75 s. In this analysis, the integration time is 10 ms and the calculation step is 5 ms. It means that the average sound level of 10 ms is calculated in every 5 ms. So if the sound lasts over 10 ms, it is possible to analyze the crackle sound itself.
Graph images are exported.
The graph of the sound level was zoomed in to the one sound at 2.25 s. This sound lasts about 25 ms.
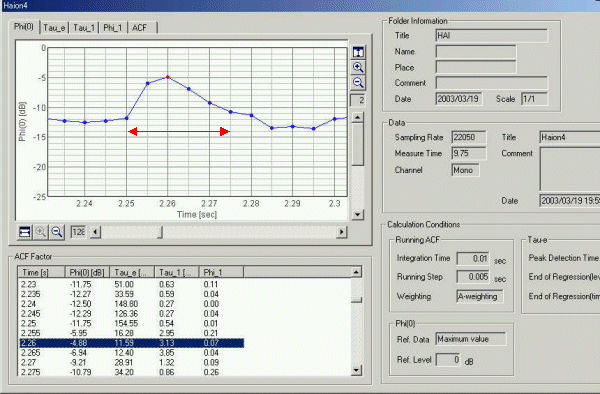
The same sound also occurs at 2.5 s. Duration of this sound is 25 ms.
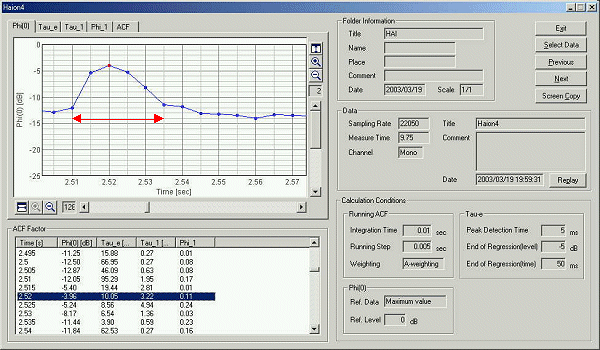
It is said that this sound is caused by the passage of air through the small airways in the lung that have become sticky and adherent. A high pitched sound is made at first and a low pitched loud sound is made at the end.
It was found that the pitch of sound is about 2 or 3 kHz until the crackle occurs, but this pitch suddenly decreases to 500 Hz at the beginning of the crackle sound. It continues decreasing to 300 and 200 Hz until the crackle sound ends. Repeat of this pitch change should have cause a very characteristic, fine, popping, and crackling sound.
If you hear this sound, it is very easy to identify. By using computer, it should also be possible to identify from other sound.
April 2003 by Masatsugu Sakurai