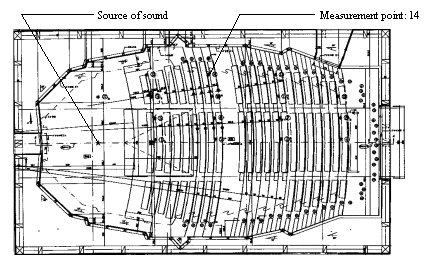
FIGURE 1. A plan of a concert hall under design
A Diagnostic System Measuring Orthogonal Factors of Sound Fields in a
scale model of concert hall
Masatugu Sakurai*, Shinichi Aizawa** and Yoichi Ando***
*Yoshimasa Erectronic Inc., Yoyogi, Sibuya, Tokyo 151-0053, Japan, and
Graduate School of Science and Technology, Kobe University, 1 Rokkodai,
Nada, Kobe 657-0013, Japan
**Yoshimasa Erectronic Inc., Yoyogi, Sibuya, Tokyo 151-0053, Japan
***Graduate School of Science and Technology, Kobe University, 1
Rokkodai, Nada, Kobe 657-0013, Japan
Abstract: A system for the sound field of a room has been
developed. It consists of a personal computer system that can measure
the impulse response of the sound field, and calculate six acoustic
parameters (SPL, ΔT1, Tsub, IACC, WIACC, and τIACC).
Measurement test using this system has been carried out in a 1/10
scale model of a concert hall.
HEADING
It is important for the concert hall to be designed an acoustic to harmonize music, hall acoustic, and audience's subjective preferences. In order to support this acoustic design, we developed the diagnostic system, which measure personal orthogonal factors.
A DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
Based on the model of auditory-brain system which consists of the autocorrelation mechanism, the interaural crosscorrelation mechanism between the both auditory pathways, and the specialization of human cerebral hemispheres, a diagnostic system was developed. The system works on PC for Windows, thus it is no need for special additional devices. After obtaining the impulse responses, four orthogonal factors including the SPL, the initial time delay gap between the direct sound and the first reflection, the subsequent reverberation time and IACC[1] are analyzed for the calculation of the scale values of global and individual subjective preference. In addition to the four factors, two more factors, τIACC and WIACC, in the interaural crosscorrelation function are figured out for evaluating the image shift of sound source and the apparent source width(ASW)[2], respectively. Also, the effective duration, τe, and fine structures of autocorrelation function of sound signals including the value of first maximum, φ1 and its delay time τ1 are analyzed. Keeping the subjectively optimal condition, this system may be utilized for automatic control of sound fields by electroacoustic systems. This system will be demonstrated at the presentation of this paper.

FIGURE 1. A plan of a concert hall under design
The system consists of two module: real-time analyzer (PC Audio) and
concert hall Acoustic analyzing System (CHAS) on a PC connected with
non-directional full-range loud speaker as output, and dummy-head
microphone as input.
The PC Audio obtains impulse response and saves it into database on PC.
The CHAS reads data from database and indicates wave form of impulse
response, then calculates factors. FIGURE 2 shows as example of the IACC
and parameters of a sound field.
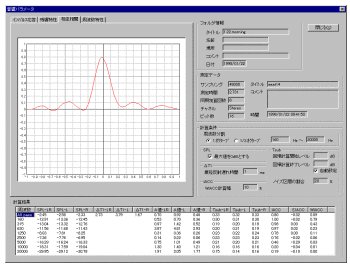
FIGURE 2. Window image from CHAS showing factor
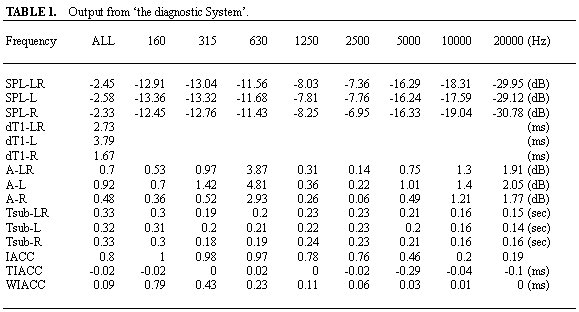
An output from CHAS indicates below on TABLE 1.
REFERENCES
1. Y.Ando, Concert Hall Acoustics. Springer-Verlag, New
York, 1985.
2. S.Sato and Y.Ando, "On the apparent source width for music sources
related to the IACC and the width of the interaural crosscorrelation
function (WIACC).", J. Acoust. Soc. Am., 102 (A), 3188, 1997.